SUOMEKSI
PÅ SVENSKA
|
 |
Finland the leader in the use of bioenergy
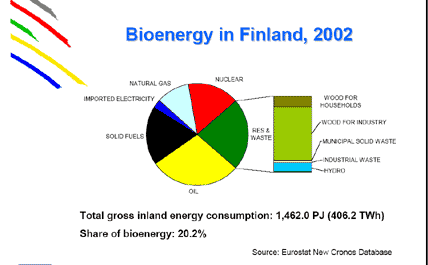 Bioenergy in Finland. Source: VTT
Biomass includes wood, wood residue, algae, cereal crops, crops containing sugar or starch, straws, grass and manure. |
Also organic waste from communities and industry are considered biofuels. Biomass releases energy when it is burned or fermenting biogas in an oxygen-free environment. Ethanol can also be produced from biomass. Burning causes CO2 emissions, but the balance can be corrected by growing more forest to compensate for the consumption. Rotting wood produces as much CO2 as burning wood.
In 2000, Finland used 76 TWh of wood-based fuels, which equals 20% of the total energy consumption in Finland. Furthermore, 11% or 8 TWh of Finnish electricity was produced with wood, a world record. Most of the wood is used for heat production both in separate heat plants and combined heat and power production (CHP). Modern technology in CHP plants yields a high total efficiency for wood use, around 90%.
In Finland, peat is classified as a slowly renewable biomass fuel. In 2001, peat accounted for almost 24% of energy produced with biomass, whereas wood yielded about 75%. Of all energy production, peat was responsible for 6.2% and wood-based energy sources for 19.5% in 2001.
|
|
 |
|
